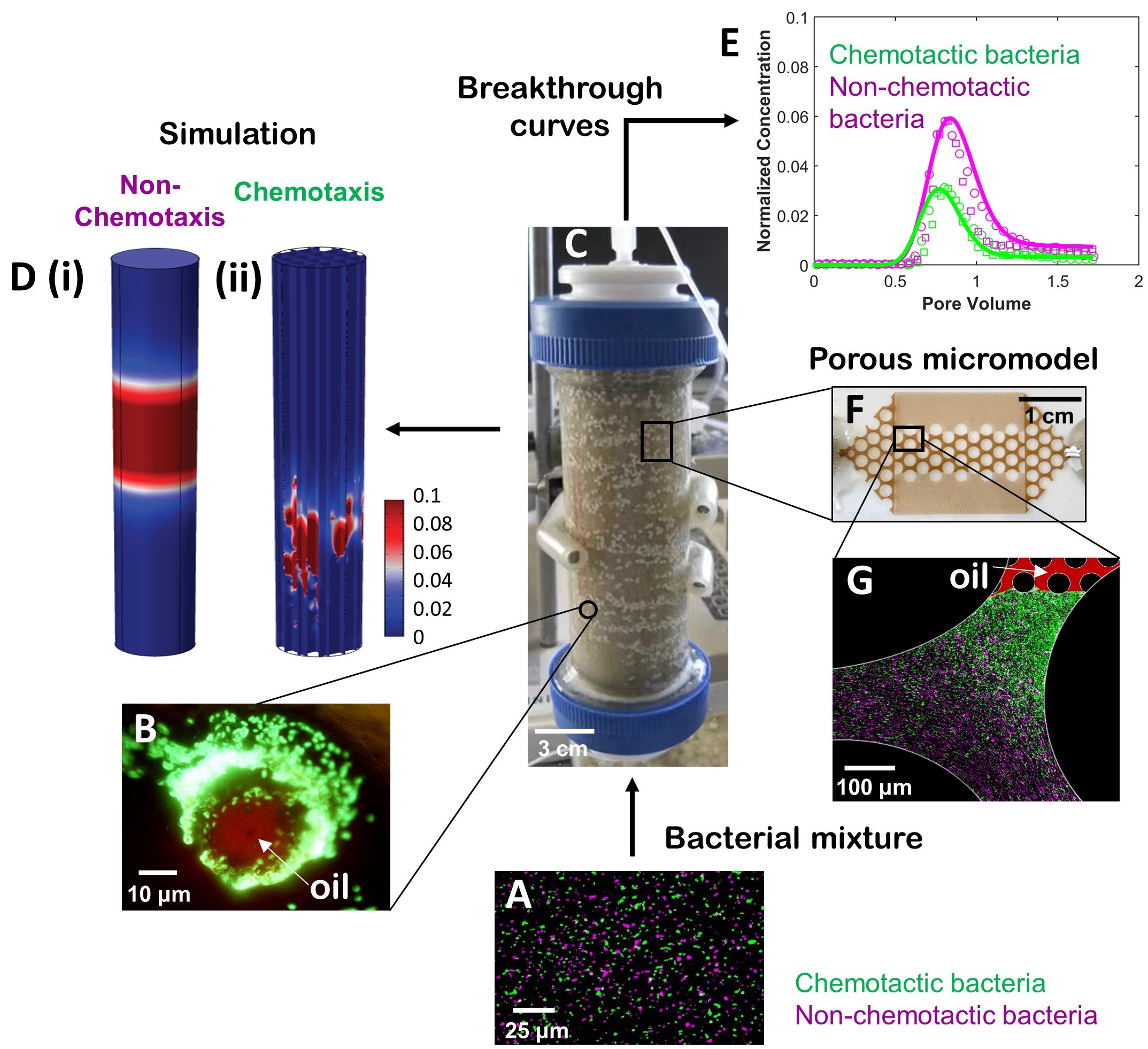
Figure 1. Transport of chemotactic bacteria through porous media with residual oil-phase chemoattractants. A. Mixture of differentially-labeled chemotactic and nonchemotactic bacteria injected as a pulse input to a chromatography column packed with sand. B. Randomly distributed within the saturated sand-pack are oily ganglia containing a chemoattractant naphthalene. C. Chemotactic bacteria advected through the column are attracted to gradients of naphthalene that emanate from the oily ganglia and are subsequently retained at the oil-water interfaces. D. Although direct observation inside the column is not feasible, computer simulations that incorporate the chemotactic response enable visualization of expected bacterial distributions within the column. The pulse input of (i) non-chemotactic bacteria spreads due to dispersion while the (ii) chemotactic bacteria tend to accumulate near naphthalene sources. E. Differences in the breakthrough curves showing bacterial concentration in the column effluent as a function of time; fewer chemotactic bacteria exit the column as compared to the non-chemotactic control. F. Microfluidic device that mimics a 2-D slice of the 3-D sand column used to test predictions from computer visualizations in panel Dii. G. Accumulation of chemotactic bacteria near oil ganglia in the pore space imaged directly using widefield microscopy.
Chemotactic microorganisms have unique features (chemical sensors and motility) that can be exploited to overcome limited bioavailability of hydrocarbon pollutants in groundwater aquifers. Quantitative evaluation of chemotaxis across multiple scales is needed to determine the conditions under which it provides an advantage to bioremediation schemes.
- P. de Anna, A. A. Pahlavan, Y. Yawata, R. Stocker, and R. Juanes, “Chemotaxis under flow disorder shapes microbial dispersion in porous media,” Nat. Phys., pp. 1-27, 2020.
- T. Bhattacharjee, D. B. Amchin, J. A. Ott, F. Kratz, and S. S. Datta, “Chemotactic Migration of Bacteria in Porous Media,” bioRxiv, no. 1, p. 2020.08.10.244731, 2020.
- R. M. Ford and R. W. Harvey, “Role of chemotaxis in the transport of bacteria through saturated porous media,” Adv. Water Resour., vol. 30, no. 6–7, pp. 1608–1617, 2006.
- R. B. Marx and M. D. Aitken, “Bacterial chemotaxis enhances naphthalene degradation in a heterogeneous aqueous system,” Environ. Sci. Technol., vol. 34, no. 16, pp. 3379–3383, 2000.
- V. Pande, S. C. Pandey, D. Sati, V. Pande, and M. Samant, “Bioremediation: an emerging effective approach towards environment restoration,” Environ. Sustain., vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 91–103, 2020.
- COMSOL Multiphysics software packages use finite element methods to solve partial differential equations that describe the transport processes of microorganisms in porous media.
- Microfluidic devices enable direct visualization of microorganisms within structured porous media designs.
- Widefield microscopy is used to observe and track individual microorganisms and the distribution of bacterial populations in microfluidic devices.
- J. S. T. Adadevoh, C. A. Ramsburg, and R. M. Ford, “Chemotaxis Increases the Retention of Bacteria in Porous Media with Residual NAPL Entrapment,” Environ. Sci. Technol., vol. 52, no. 13, pp. 7289–7295, 2018.
- J. S. T. Adadevoh, S. Ostvar, B. Wood, and R. M. Ford, “Modeling Transport of Chemotactic Bacteria in Granular Media with Distributed Contaminant Sources,” Environ. Sci. Technol., vol. 51, no. 24, pp. 14192–14198, 2017.
- X. Wang, L. M. Lanning, and R. M. Ford, “Enhanced Retention of Chemotactic Bacteria in a Pore Network with Residual NAPL Contamination,” Environ. Sci. Technol., vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 165–172, 2016.
